What is the difference between PVC wood door and melamine wood door
The main differences between PVC wood doors and melamine wood doors lie in their material composition, durability, water resistance, appearance, and cost. Here’s a detailed comparison:
1. Material & Construction
PVC Wood Door
- Core Material: Usually made of solid wood, engineered wood (MDF, particleboard), or foam-filled honeycomb structure.
- Surface Coating: Covered with a PVC laminate or PVC film, which is waterproof and flexible.
- Edges: Sealed with PVC wrapping for full water resistance.
Melamine Wood Door
- Core Material: Typically particleboard or MDF (Medium-Density Fiberboard).
- Surface Coating: Coated with melamine-impregnated decorative paper (thermoset plastic resin).
- Edges: Usually finished with PVC edge banding or melamine edges (less waterproof than full PVC wrap).
2. Durability & Maintenance
- PVC Wood Door:
- Resistant to scratches, stains, and chemicals.
- Easy to clean (wipe with damp cloth).
- Does not peel or fade easily.
- Melamine Wood Door:
- Scratch-resistant but less durable than PVC.
- Can chip or delaminate at edges over time.
- More prone to heat damage (discoloration from hot objects).
3. Appearance & Finish
- PVC Wood Door:
- Available in high-gloss, matte, woodgrain, and textured finishes.
- More realistic 3D wood-like textures.
- Can be molded into curved designs.
- Melamine Wood Door:
- Usually smooth, matte, or semi-gloss finish.
- Limited to flat surfaces (no curves).
- Less natural-looking than high-end PVC laminates.
Which One Should You Choose?
- For bathrooms, kitchens, or high-humidity areas → PVC wood door (fully waterproof).
- For bedrooms, offices, or dry areas on a budget → Melamine wood door.
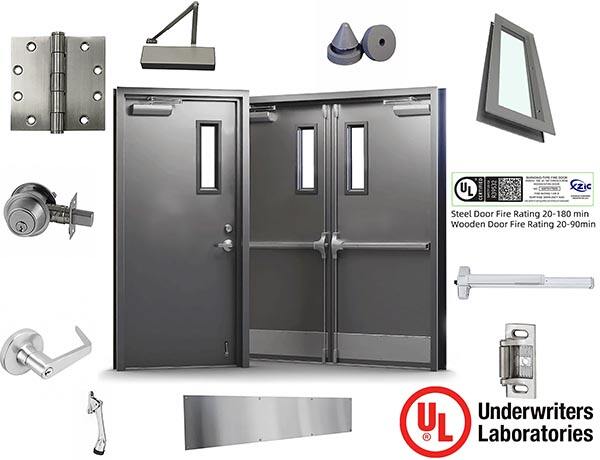
Recommended Products
Hot News
-
UL fire door Regulatory and Certification Requirements
2025-08-08
-
What are the types for fire Doors?
2025-07-12
-
Why Hollow Metal Doors Are a Cost-Effective Long-Term Solution for Businesses
2025-07-23
-
What’s the price difference for UL LISTED FIRE DOOR of mahogany/oak/ beech/walnut veneer finish compared with Formica /TAK/ Wilsonart Laminated finish ?
2025-07-31
-
What is MDF (medium-density fiberboard) Door?
2025-06-15
-
Essential Aspects of UL Metal Fire Door Inspection
2024-01-02
-
XZIC Delivers Superior Quality UL Fire Doors to Our Valued Client in Qatar
2024-01-02
-
Can hollow metal doors be insulated?
2024-01-02
 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 BG
BG
 NL
NL
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 EL
EL
 IT
IT
 KO
KO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RO
RO
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 TL
TL
 IW
IW
 ID
ID
 UK
UK
 VI
VI
 TH
TH
 FA
FA
 AF
AF
 MS
MS
 SW
SW
 BE
BE
 UR
UR
 BN
BN
 KM
KM
 LO
LO
 LA
LA
 MI
MI
 MN
MN
 MY
MY
 KK
KK
 MG
MG
 SU
SU
 TG
TG
 UZ
UZ
 KY
KY
 XH
XH